Edited by: Michelle Macdonald
Are you ever confused about what role cardio training should play in your overall fitness journey? Ever wondered what that magic combination is where everything aligns and leads you to see the results you’re hoping for across the board? At The Wonder Women, our mission is to educate and empower women over 40, reshaping the way they approach their health and well-being. Cardiovascular training is a cornerstone of any fitness regimen, and especially for women as they age. It goes beyond just shedding weight; it’s about nurturing a healthy heart, robust muscles, and a vibrant life. Heart disease is more common in older women, and it is the leading cause of death for women over 40, especially after menopause. This comprehensive guide delves into effective cardio training for women, elucidating the science behind it, its influence on energy balance, and strategies for achieving your fitness aspirations.
The Science of Cardiovascular Training (CVT)
Cardio Training and Cardiovascular Health
At the core of promoting heart health in women over 40 lies the fundamental role of cardio training. Cardiovascular health refers to the well-being of the heart and blood vessels, which are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. CVT strengthens the heart, improves blood vessel flexibility, and boosts the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. This is not just about endurance; it’s about having a healthy, efficient, and tireless heart. Cardio workouts are the engine that keeps the cardiovascular system running smoothly.
Research conducted by Elie Fiogbé and colleagues found that cardio training benefits oxygen transport and muscle function. Their systematic review of seven randomized controlled trials found that endurance training, with its focus on sustained, rhythmic movements, was particularly effective. It enhanced microvascular blood flow, optimized the delivery of oxygen to meet the body’s demands, and strengthened muscle oxidative capacity and saturation.
Effective cardio training for women requires an understanding of how muscles respond to different forms of exercise. Muscles are highly adaptable and constantly reshape themselves based on the training they receive.
HIIT
A comprehensive study conducted by David C. Hughes, Stian Ellefsen, and Keith Baar offers valuable insights into these changes. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is particularly effective at increasing the number and function of mitochondria within muscle cells, which are the cellular powerhouses responsible for energy production. This means that your muscles can work more efficiently during endurance exercises.
LSD
Prolonged low-intensity and high-volume endurance exercise, also known as long slow-distance (LSD) training, is also effective at increasing mitochondria in muscle cells and expanding their energy production capacity. This helps your muscles endure longer during cardio workouts.
Endurance Training
Endurance training also enhances glycogen storage in muscle cells, which is a crucial energy source during exercise. While both HIIT and LSD training lead to valuable muscle adaptations, they do so in different ways. HIIT is better at refining mitochondrial respiration and function, while LSD training is better at increasing mitochondrial content. It’s important to note that individual responses to endurance training can vary. Some people thrive on HIIT, while others find LSD training more effective.
Take a look at the positive impacts of different cardio training methods on cardiovascular health:
| Cardio Training Method | Positive Impacts on Cardiovascular Health |
| Moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) | – Improves aerobic fitness by increasing VO2max. |
| High-intensity interval training (HIIT) | – Provides similar cardiovascular benefits to MICT in a shorter amount of time. |
| Fartlek training | – Combines elements of MICT and HIIT for a varied and challenging workout. |
| Tabata training | – A type of HIIT that involves alternating between 20 seconds of high-intensity exercise and 10 seconds of rest for eight rounds. |
Effective Cardio Training and Energy Levels
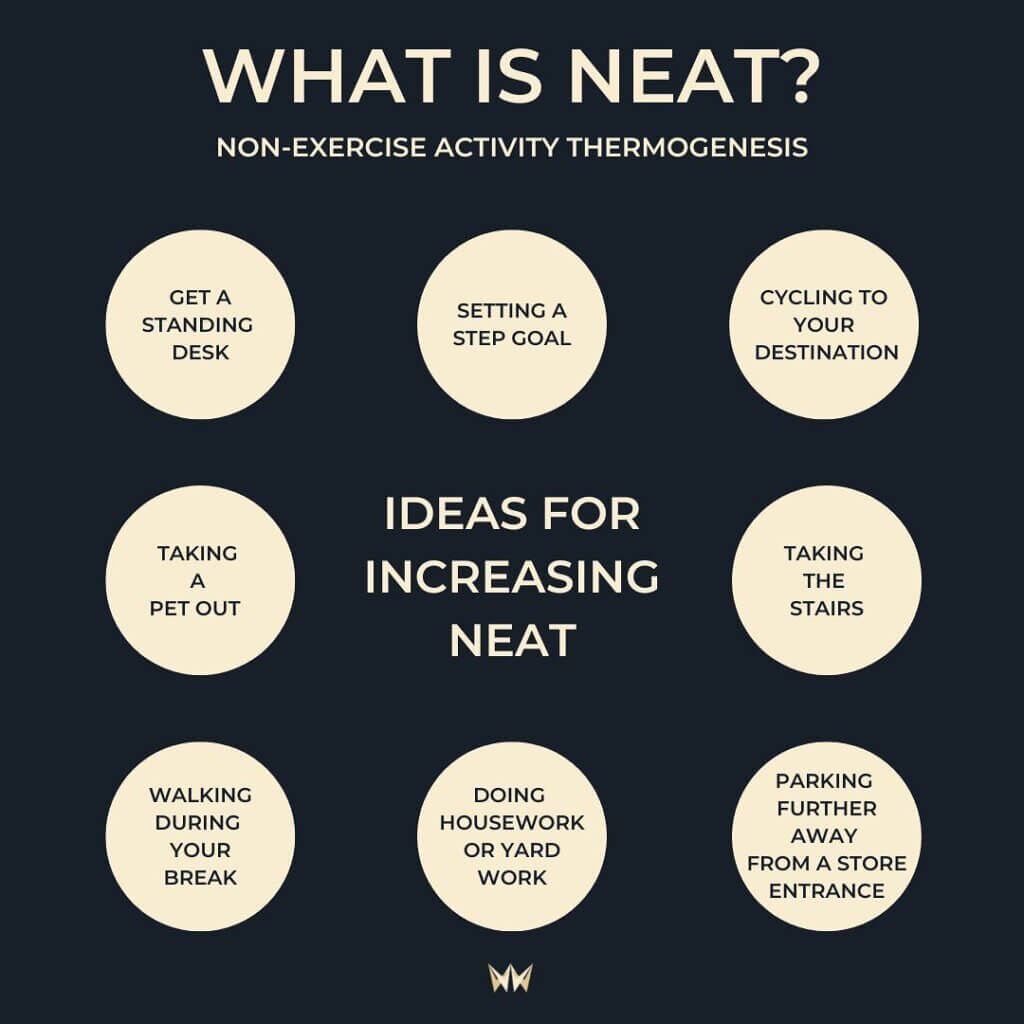
Cardiovascular training plays an important role in managing blood sugar levels, energy levels, and weight. A consensus statement found that cardio exercise improves insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, with high-intensity interval training (HIIT) being more effective than moderate-intensity training. This is based on a review of clinical trials, case reports, reviews, and meta-analyses. Cardio training also affects energy balance. Effective fat loss requires burning more calories than you consume. You can achieve this balance by reducing calorie intake, increasing non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT), or increasing cardio. NEAT is the energy you burn through everyday activities other than sleep, eating, or structured exercise. It plays a vital role in energy balance and weight management.
When building muscle, you need to be in a positive energy balance, which means eating more calories than you burn. However, you should still do cardio training to maintain heart health and improve your insulin sensitivity.
A study on fat metabolism during aerobic exercise found that cardio training enhances fat metabolism by increasing the utilization of fat for energy during exercise. This leads to reduced body fat, improved insulin sensitivity, and increased expression of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation. This study highlights that cardiovascular training is key to enhancing fat metabolism, reducing body fat, and decreasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- The consensus statement found that cardio exercise improved insulin sensitivity by an average of 13% and blood sugar control by an average of 10%. HIIT was more effective than moderate-intensity training at improving insulin sensitivity.
- The fat metabolism study found that cardio training increased the utilization of fat for energy during exercise by an average of 25%. This led to a reduction in body fat of an average of 5%.
Overall, research shows that cardiovascular training is an effective way to improve blood sugar control, energy levels, fat loss, and overall health.
Cardio Training for Fat Loss
We firmly believe in a balanced approach to cardio training for fat loss. It’s not solely about dedicating extended hours to aerobic exercise; rather, it’s about making your workouts sustainable and enjoyable. Creating a cardio routine tailored to your specific goals and lifestyle is the best way to do just that.
The Role of Diet in Conjunction with Cardio Training
Diet and cardio training is a dynamic duo, working hand in hand to help you reach your fitness goals. A well-balanced diet is just as important as cardio training. Together, they help you burn more calories than you consume, which is necessary for fat loss.
Complex carbohydrates give you energy for workouts, protein helps your muscles repair and grow, and healthy fats are essential for overall health. There are no “bad foods,” but it’s important to eat the right types, amounts, and timing of foods for your body’s needs. The better you understand your body and nutritional needs, the better you can create meals and food timing that help you reach your goals.
Importance of Tracking Heart Rate During Cardio Sessions
Tracking your heart rate during cardio workouts is important, especially for women over 40. It helps you ensure that you are working out at the right intensity for your cardiovascular health and fitness goals.
There are five main heart rate zones for exercise:
Zone 1: 50-60% of maximum heart rate (MHR)
Zone 2: 60-70% of MHR
Zone 3: 70-80% of MHR
Zone 4: 80-90% of MHR
Zone 5: 90-100% of MHR
Fat loss is typically in Zone 2 and Zone 3. This is because your body burns a higher percentage of fat for energy at lower intensities. However, you need to work out for a longer time in these zones to burn the same number of calories as you would at a higher intensity.
Moderate-intensity exercise (Zone 2 and Zone 3) is also good for improving cardiovascular health. It strengthens your heart and lungs and helps to lower your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Vigorous-intensity exercise (Zone 4 and Zone 5) is good for increasing calorie burn and improving cardiovascular fitness. However, it is important to note that vigorous-intensity exercise is not recommended for everyone, especially women over 40 who are new to exercise.
To find your maximum heart rate, subtract your age from 220. With a heart rate monitor, you can track your heart rate during workouts to ensure you are working at the right intensity for your fitness goals.
Here is a table that summarizes the different heart rate zones and their benefits:
| Heart rate zone | % of MHR | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 | 50-60 | Active recovery, light cardio |
| Zone 2 | 60-70 | Fat burning, improved cardiovascular health |
| Zone 3 | 70-80 | Fat burning, improved cardiovascular fitness |
| Zone 4 | 80-90 | Increased calorie burn, improved cardiovascular fitness |
| Zone 5 | 90-100 | Maximal effort, used in high-intensity interval training (HIIT) |
If you are new to exercise, start by working out in Zone 2 or Zone 3 for 20-30 minutes, 3-4 times per week. As you get fitter, you can gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. It is also important to listen to your body and rest when you need to.
Understanding the Fat-Burning Zone
The fat-burning zone is around 70-75% of your maximum heart rate. It is the best intensity for burning fat, even though many think that cardio must be high-intensity to be effective.
Walking is a good way to get into the fat-burning zone. It may take 10 minutes for your heart rate to reach this range, so you may want to start with a 40-minute walk or a few sprints.
When your heart rate is in the fat-burning zone, your body releases fat from cells (fat mobilization) and transports it to other cells to be burned (oxidation).
To maximize fat burning, create a calorie deficit through diet and eat meals with intervals in between. Doing cardio in the morning can also help because your cortisol levels are naturally higher, which can promote fat mobilization.
Structuring Your Cardio Routine
Deciding how to structure an effective cardio routine to maximize fat loss can seem overwhelming but it doesn’t have to be. The Wonder Women can provide the framework you need to create a routine that brings you the results you desire.
Starting with the Basics
Start with four cardio sessions per week, each for 20 minutes. Choose activities you enjoy, as this will make it more likely that you will stick with your routine. To burn the most calories, focus on activities that use your large leg muscles.
Breaking Through Plateaus
Everyone hits plateaus on their fitness journey. These can be caused by many things, such as poor sleep, digestion, stress, your menstrual cycle, fluid retention, weather changes, and changes in your diet. To overcome plateaus, increase your cardio sessions to five times per week, each for 25 minutes. This increased frequency and duration can help you break through plateaus.

Increasing the Intensity
To keep progressing towards your fitness goals, gradually increase the length of your cardio sessions by 5 minutes at a time. Over time, aim for 40-45 minutes of cardio per day. This will help you reach your fitness goals more quickly.
Push Further
If you want to challenge yourself even more and reach your full fitness potential, you can try doing 6 days per week of 40-45 minutes of cardio. However, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid injuries.
| Stage | Frequency | Duration | Intensity |
| Starting with the Basics | 4 times per week | 20 minutes per session | Moderate |
| Breaking Through Plateaus | 5 times per week | 25 minutes per session | Moderate |
| Increasing the Intensity | 5 times per week | 30-40 minutes per session | Moderate to vigorous |
| Push Further | 6 times per week | 40-45 minutes per session | Vigorous |
Staying Active Beyond Cardio
Increasing activity levels across the board is where the true transformation of our health and fitness takes place. While incorporating cardio into your routine is undoubtedly a significant step towards fat loss and cardiovascular health, it’s only one piece of the puzzle. True lifestyle changes take place with our overall lifestyle choices and the consistency with which we integrate physical activity into our daily lives. The journey to a healthier and more active life requires us to make holistic changes.
Daily Step Goals (8,000 steps a day)
One powerful strategy to stay active beyond cardio is to set daily step goals. Aiming for 8,000 steps a day can make a big difference. These steps aren’t just about reaching a number; they represent an active lifestyle. Achieving this daily step goal ensures that you’re not just sitting around all day. Instead, you’re constantly moving, which has many benefits for your health and well-being. It’s a simple yet effective way to boost your overall activity level and reach your fitness goals.
Your daily step count should not include your cardio workouts.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Life
It’s easier than you might think to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine. You can do it at home, at work, and even during your leisure time. Small changes, like taking the stairs instead of the elevator, standing instead of sitting, or taking a short walk during breaks, can make a big difference over time.
Here are some practical tips and creative ideas for infusing your daily life with physical activity:
- Take breaks to stand up and move around every 30 minutes.
- Do some bodyweight exercises at home while you’re watching TV.
- Dance around your living room while you’re cooking or listening to music.
- Take advantage of active transportation options, like walking, biking, or taking public transportation instead of driving.
- Find a workout buddy to motivate you and keep you accountable.
Connecting Cardio Training and Daily Activity
Cardio training and daily activity work together to enhance your fitness journey. Cardio workouts get your heart rate up and improve your endurance, while daily activity keeps your metabolism going and helps you manage your weight.
When you combine cardio training and daily activity, you’re creating a powerful synergy that can lead to improved health, sustained fat loss, and a more energized lifestyle.
A Balanced Approach to Fitness
The Wonder Women advocate for a balanced approach to fitness that combines cardio training, dietary adjustments, and daily activity. This approach empowers you to take control of your well-being and achieve your fitness goals.
To lose weight, you need to create a calorie deficit. This means burning more calories than you consume. To lose one pound, you need to create a 3,500-calorie deficit. This translates to a deficit of 1,000 calories per day for those aiming to lose one to two pounds per week.
To create a calorie deficit, you can reduce your caloric intake, increase your physical activity, or do both. If your maintenance level is 2,200 calories per day, reducing your caloric intake by 500 and burning 500 calories through exercise can help you reach your goals.
A Well-Rounded Fitness Plan
Your fitness plan should be well-rounded and include a variety of activities, such as:
- Cardiovascular exercise: Aim for three to five days of cardio workouts per week, each lasting 10-60 minutes. Training in Zone 3 or higher will allow for shorter durations. The frequency and duration of your cardio workouts will depend on your fitness goals, such as building muscle or burning fat.
- Strength training: Aim for three to five days of strength training per week, with a duration of 45-60 minutes per session.
- Flexibility and stretching: Incorporate daily stretching and flexibility exercises to maintain suppleness, for 10-15 minutes per session.
- Rest: Make sure to include at least one to two days of rest per week to allow your body to recover. On these days, you can engage in active recovery exercises such as yoga or gentle stretching.
| Activity | Frequency | Duration |
| Cardiovascular exercise | 3-5 days per week | 10-60 minutes per session |
| Strength training | 3-5 days per week | 45-60 minutes per session |
| Flexibility and stretching | Daily | 10-15 minutes per session |
| Rest | 1-2 days per week | N/A |
We firmly believe that fitness is not about quick fixes but about instigating lasting changes. Our holistic approach is designed to make your fitness journey enjoyable, sustainable, and effective, allowing you to seize control of your health and well-being with confidence.

